
Nothing can impact an investor’s success more than discipline. Warren Buffett noted that “the stock market is a device for transferring money from the impatient to the patient.” In studying the returns of various asset classes, JP Morgan made the startling conclusion that the average investor is the worst performing class:
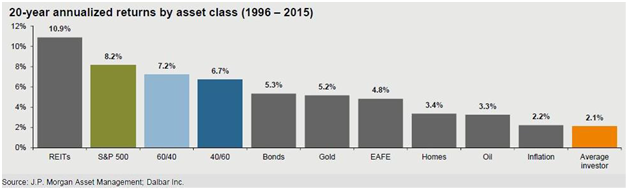
Think on that for a moment…the average investor in the world underperformed every single major asset class out there
This has been confirmed over and over in various market studies. Fidelity Investments conducted a study on their Magellan Fund from 1997-1990 during Peter Lynch’s tenure. His average annual return during this period was an incredible 29%. This is a remarkable return over a thirteen year period. Given all of that, you would expect that the investors in his fund made substantial returns over that period. However, what Fidelity Investments found in their study was shocking. The average investor in the fund lost money
For those of us that trade options, particularly options under a defined strategy, this should be a stark reminder to stick to a plan, don’t go off plan, and certainly remain patient when patience is called for. While this may be easy to say though, in practicality what does this mean? For me, there are four points I try to keep in mind:
1. When you enter a trade, know your exit points before entering
This seems simple, but in actuality can be quite difficult to stick to. For instance, we might say our target gain in an earnings straddle trade is fifteen percent. Two days in though we’re at an 11% gain and the price has moved 8% from our strike. Do we take and roll? Let it ride to get closer to 15% and risk retracement? Do we exit and move to the next trade? Does this change if we’re 8 days from expiration as opposed to 2? How does it change if overall market volatility has dropped or increased dramatically? And what is the 15% target even based on? Has it been back tested, is it based on “experience,’ or does it just seem like “a good target?”
A lot of options traders will say it just depends on a lot of factors, the current market, and that they have developed a good “sense” for when to make these decisions. And while it is indisputable that there certainly are better traders than others that have a better “sense” of doing things, anyone who falls into this trap is certainly both (a) deluding themselves and (b) costing themselves profits.
Psychology studies on humans on this topic are fascinating. We have an incredible ability to deceive ourselves into thinking we’re better at things than we are, that we are making decisions based off of empirical and factual evidence when we are not, and that we always will make the same decisions in the same situations. In reality, what you had for breakfast will impact your decisions. How much you are up or down will impact your decisions – and this is true EVEN IF you consciously realize that you being up or down might impact your decision.
There are several great books that speak to how our minds work and are impacted by things we don’t even realize:
- Impossible to Ignore, by Dr. Carmen Simon
- Thinking Fast and Slow, by Daniel Kahneman
- Influence, by Robert B. Cialdini
- The Power of Habit: Why We Do What We Do in Life and Business, by Charles Duhigg
as well as others. What they all have in common is noting that basically we are all morons that have deluded ourselves into thinking we have more control over our thought processes than we really do.
The only
Your trading results will improve.
2. Prior to entering an order, know the highest price you are willing to pay
Slippage cuts on both sides of the trade.
This point is a close corollary to the first, and may seem obvious, but I cannot count the number of times prices are chased, often simply because we feel a need
Perhaps the most common mistake I see with this is not sticking to a cap in entering a trade, but rather failing to consider that same slippage on the cost of exiting and calculating that at the start.
For instance, let us assume the current mid-point on a straddle we plan on buying is $1.00 and we have a 10% profit target. We enter our order and are not getting a fill and think to ourselves that we would enter this trade, with an acceptable risk profile, as long as we still have an expected return of 7%. So we bump our order to $1.01 and still don’t get a fill. Then we bump to $1.02 and do get filled and think we reduced our expected gain from 10% to 8% and feel good about being in the trade. Only our expected gain is not 8% it is 6%much
This applies also to trade alerts, not just your own trades. If you are consistently getting fills $0.05 off of an “official” trade alert, don’t assume that you will only find that inefficiency on the trade entering side. You most likely will encounter it exiting too and need to account accordingly.

3. Be willing to stay in cash
To me, this is by far the hardest discipline, particularly after a series of losses. If we are looking at trade that has profited when relative value was below 4% and loses when above 5% then WAIT until it gets below 4% to enter. It is tempting to say “well I’m below that 5% loss point, we don’t have any trades on, we can’t make money if we’re not trading, so let’s go ahead and enter.” Unfortunately this has simply reduced a strategy to gambling. Sure, we may win sometime and lose others, but we are not here to gamble. We are here to make money, and that means sticking to what we know works.
This can be incrediblymissed
If you ever feel the urge to enter a trade, you know is questionable, step away, talk to someone, do something to get away from your trading screen.
4. Be able to move on from losses AND gains
This is the hallmark of a good trader. Anyone who watches poker regularly has seen a player go on tilt. Going on tilt simply means a player is on a “streak” and stops doing what they are supposed to be doing and goes on feel, increases leverage, or generally starts acting stupid. What’s amazing is that poker players, even very good ones, go on tilt just as often on a winning streak as they do on a losing streak.
When losing in trading it is tempting to want to up your allocation size so you can “make up” for those past losses, or from point three above, just to trade more maybe when you shouldn’t. When winning it’s tempting to keep jumping back in, or worse, letting gains “ride” that you should have closed out from (point 1).
No matter how well we execute our trades, there will be losing trades because we are playing a probability game. Trading, particularly in options, is a business based on probability. And probability means that sometimes we get what we want and sometimes we don’t. That’s the nature of this business. Then sooner we accept that, the better we can operate as a business.
One of the hardest things to do is to ignore your gains and losses on a day to day basis. I’m not advocating not watching your portfolio because if you lose 5% a month, following the same strategy, for a full year then something is wrong (maybe – could still be a viable strategy with a horrible streak, but you need to definitely dig into it some). But to be able to stick to your trading plan one must
The simplest way to do this is to follow the previous three points. If you know when to get in a trade and how not to over pay, know when you are supposed to go out, and are not over trading just to trade, then you can look at your gains and losses and say “I did everything right” and accept the results. I find that I get mired in results the most when I deviated from the plan and have to say “I messed up.”
Concluding Remarks
Vanguard commissioned a study to look at investment advisors, the fees they charge, and the services they provide. Surprisingly, they concluded that the single most valuable service an advisor provides to clients relates to investor psychology and staying on track. Not picking “winning” investments, not developing a proper tax plan, not financial planning – but rather preventing your average investor from underperforming every asset class out there because the investor won’t stick to a plan that was developed.
If you would like to talk to an investment advisor or Certified Financial Planner™ Professional feel free to contact me ( cwelsh@lorintinecapital.com ) or my partner Jesse Blom ( jblom@lorintiencapital.com ) at anytime.
If you have any questions you would like answered and do not want to reach out to us directly, feel free to make a posting on SteadyOptions. We also answer questions on Quora and any of us here would be happy to answer your questions through that forum. Feel free to follow us:
What Is SteadyOptions?
Full Trading Plan
Complete Portfolio Approach
Diversified Options Strategies
Exclusive Community Forum
Steady And Consistent Gains
High Quality Education
Risk Management, Portfolio Size
Performance based on real fills
Non-directional Options Strategies
10-15 trade Ideas Per Month
Targets 5-7% Monthly Net Return
Recent Articles
Articles
Pricing Models and Volatility Problems
Most traders are aware of the volatility-related problem with the best-known option pricing model, Black-Scholes. The assumption under this model is that volatility remains constant over the entire remaining life of the option.
By Michael C. Thomsett, August 16

- Added byMichael C. Thomsett
- August 16
Option Arbitrage Risks
Options traders dealing in arbitrage might not appreciate the forms of risk they face. The typical arbitrage position is found in synthetic long or short stock. In these positions, the combined options act exactly like the underlying. This creates the arbitrage.
By Michael C. Thomsett, August 7

- Added byMichael C. Thomsett
- August 7
Why Haven't You Started Investing Yet?
You are probably aware that investment opportunities are great for building wealth. Whether you opt for stocks and shares, precious metals, forex trading, or something else besides, you could afford yourself financial freedom. But if you haven't dipped your toes into the world of investing yet, we have to ask ourselves why.
By Kim, August 7

- Added byKim
- August 7
Historical Drawdowns for Global Equity Portfolios
Globally diversified equity portfolios typically hold thousands of stocks across dozens of countries. This degree of diversification minimizes the risk of a single company, country, or sector. Because of this diversification, investors should be cautious about confusing temporary declines with permanent loss of capital like with single stocks.
By Jesse, August 6

- Added byJesse
- August 6
Types of Volatility
Are most options traders aware of five different types of volatility? Probably not. Most only deal with two types, historical and implied. All five types (historical, implied, future, forecast and seasonal), deserve some explanation and study.
By Michael C. Thomsett, August 1

- Added byMichael C. Thomsett
- August 1
The Performance Gap Between Large Growth and Small Value Stocks
Academic research suggests there are differences in expected returns among stocks over the long-term. Small companies with low fundamental valuations (Small Cap Value) have higher expected returns than big companies with high valuations (Large Cap Growth).
By Jesse, July 21

- Added byJesse
- July 21
How New Traders Can Use Trade Psychology To Succeed
People have been trying to figure out just what makes humans tick for hundreds of years. In some respects, we’ve come a long way, in others, we’ve barely scratched the surface. Like it or not, many industries take advantage of this knowledge to influence our behaviour and buying patterns.

- Added byKim
- July 21
A Reliable Reversal Signal
Options traders struggle constantly with the quest for reliable
By Michael C. Thomsett, July 20

- Added byMichael C. Thomsett
- July 20
Premium at Risk
Should options traders consider “premium at risk” when entering strategies? Most traders focus on calculated maximum profit or loss and breakeven price levels. But inefficiencies in option behavior, especially when close to expiration, make these basic calculations limited in value, and at times misleading.
By Michael C. Thomsett, July 13

- Added byMichael C. Thomsett
- July 13
Diversified Leveraged Anchor Performance
In our continued efforts to improve the Anchor strategy, in April of this year we began tracking a Diversified Leveraged Anchor strategy, under the theory that, over time, a diversified portfolio performs better than an undiversified portfolio in numerous metrics. Not only does overall performance tend to increase, but volatility and drawdowns tend to decrease: